The implementation of the SAP® GRC Access Control tool in the Sigma organization was the first implementation of SAP® GRC Access Control by Inprosec in Mexico. This implementation had a difference with respect to other SAP® GRC AC implementation cases since it was the first one in which the User Access Review (UAR) module was implemented to comply with the audit requirement for access recertification. The project had a duration of 5 months starting in November 2018 and would end in March 2019.
Sigma is a Mexican multinational company involved in the production and distribution of refrigerated food. It is headquartered in the municipality of San Pedro, in the Metropolitan Zone of Monterrey, Nuevo Leon, Mexico. It has operations in more than 20 countries including Mexico, the United States and Europe.
The challenge
The difficulty of the project was on the one hand to adapt the current process that was being used on a day-to-day basis at Sigma to the technology offered by the GRC system. This point is very important since we are not only talking about a technological change, but also included the need for an organizational or governance change. Another challenge that the project sought to cover was related to the role management process, where risk management was to be included in the process for the creation/modification of roles.
Sigma’s organization had a Risk Matrix that was being reviewed by an external audit. This matrix was the first step in the creation of Sigma’s Risk Matrix, which was a step forward in Sigma’s Risk Management.
Inprosec Solution
Inprosec’s solution was to carry out a project dividing the phases according to the tool to be implemented:
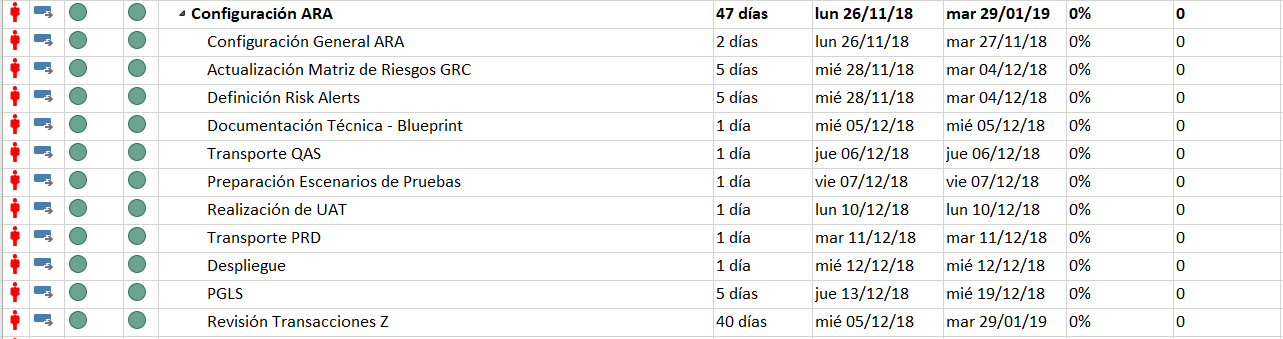
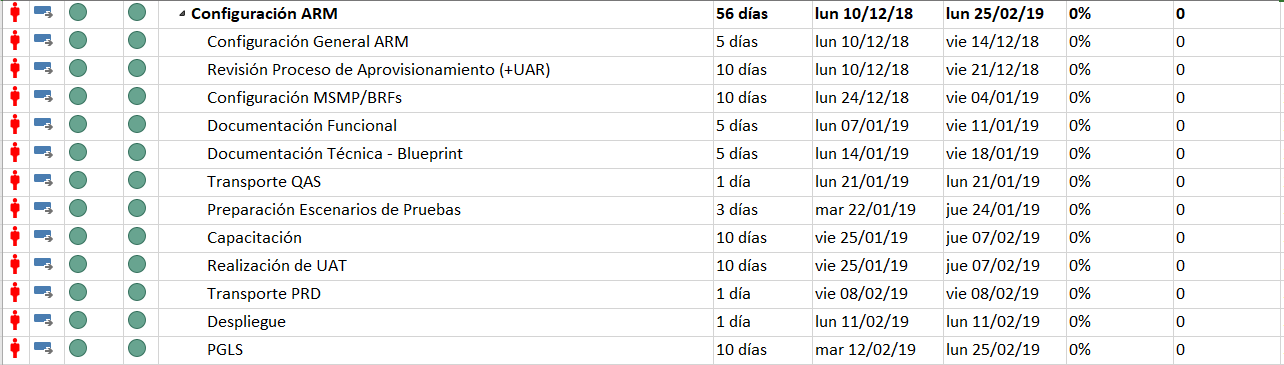
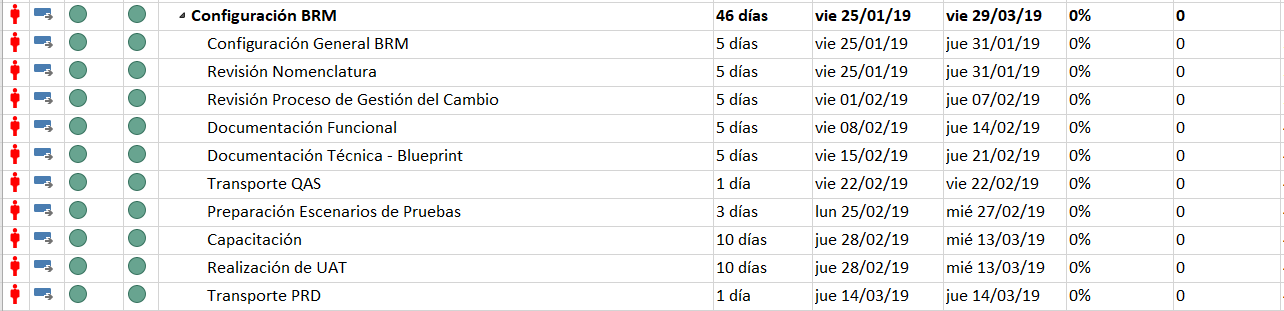
The Objectives/Milestones sought for the first phase were:
- Updating the Risk Matrix to the latest version of the SAP® standard.
- Activation of Risk Alerts
- Analysis of Z Transactions to be included in the Risk Matrix.
- Creation of Compensating Controls
- Creation of Sigma Risk Matrix
- Stakeholder training.
The Objectives/Milestones sought for the second phase were:
- Configuration of “Workflows” for Creation, Modification, Deletion of Users in SAP®.
- Password Reset
- Access Request for Firefighters
- Roles Recertification (User Access Reviews).
- Stakeholder Training.
The Objectives/Milestones sought for the third phase were:
- Configuration of Workflows for Role Creation and Modification in SAP®.
- Mass Roles Upload (based on the new role model that was being implemented).
- Nomenclature Automation
- Training to interested parties.
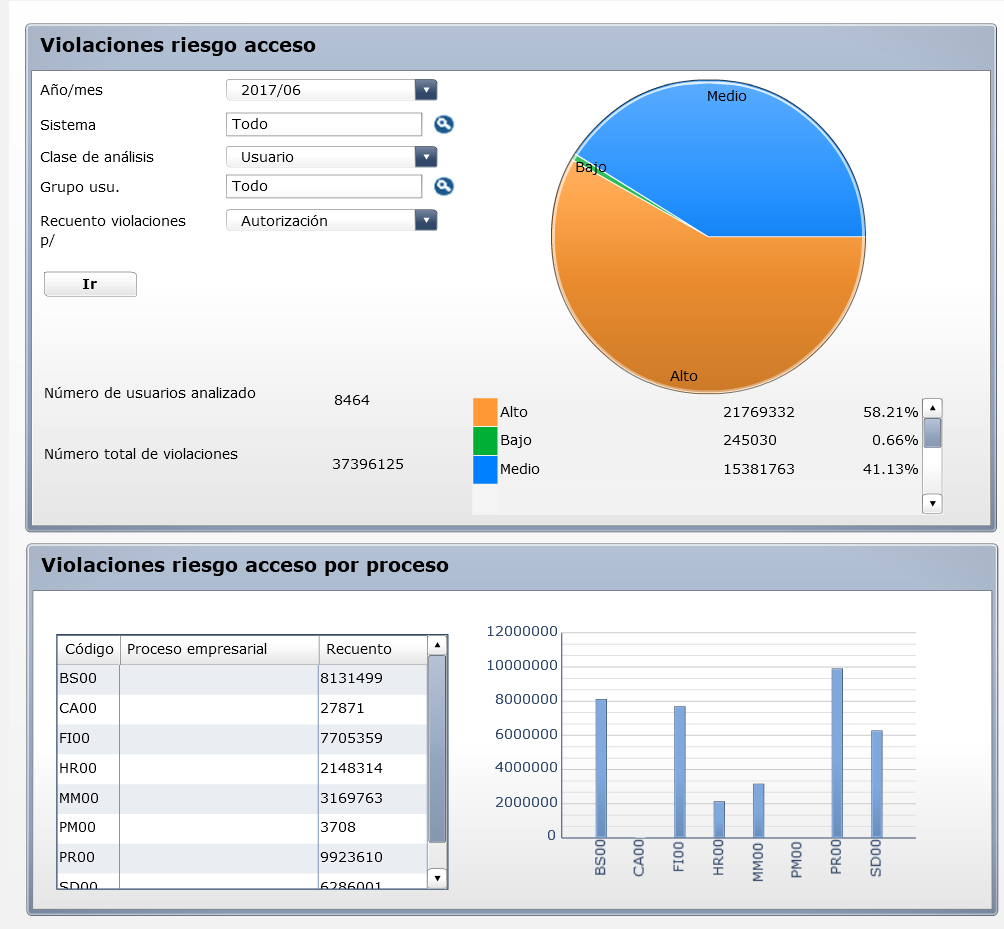
In relation to Phase I, a total of 13 Risk Alerts were defined, focused on IT scenarios and which would communicate on a daily basis all the risks in which the execution of the Transactions involved in said risks would be confirmed. The option was marked that those users with an assigned compensating control would be excluded from such automatic communication.
Another major tool that is frequently used in Sigma was the use of the standard SAP® Dashboard where all the details of users and risks existing in the Sigma organization can be identified:
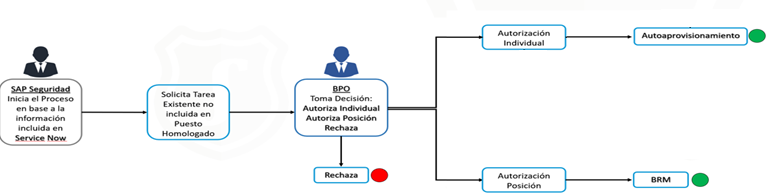
During Phase II, work was done on everything related to user provisioning. In order to allow greater flexibility throughout the provisioning process, a small form was created which, depending on the response, would progress through the process in one way or another.
- The individual authorization option meant that access was only required for one user of the item.
- The authorize position option meant that access had to be given to all users who were part of the position, so this selection meant creating a BRM request for the position’s role maintenance.
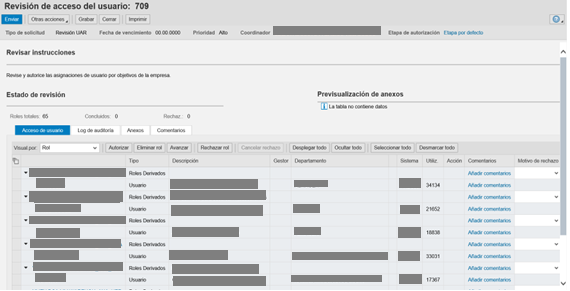
In addition to what had already been mentioned about ARM previously, Phase II also included the implementation of the User Access Review functionality that allowed to comply with the access recertification process that was being required by Audit. In the case of Sigma, and due to the fact that it was in the process of re-engineering the role model, this implementation was simpler since the recertification process would be executed only for the positions that had been approved for the time being:
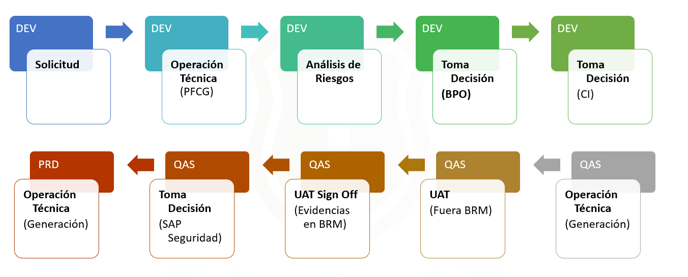
Finally, during Phase III, the implementation of the Business Role Management tool was carried out, which allows creating and modifying roles in SAP® through SAP® GRC. A complete flow was established that could comply with the change management process that existed in Sigma:
We worked with a single active process in BRM and that allowed not only the design and creation of the role in the Development environment, but also allowed its transport to the Quality and Production systems aligning it with a process that supported change management. An important point was the deactivation of any kind of role deletion activity through BRM to avoid any kind of impact on the satellite systems connected to SAP® GRC Access Control.
Results
The implementation of the Access Control tool in Sigma was a success from several points of view: a risk matrix was activated that met the audit requirements and Sigma’s needs, an agile provisioning process was generated for user creations and modifications in SAP®, a role management process was implemented that included visibility of possible SoD risks that could be appearing as part of the creation/maintenance process, an access recertification process was generated that met the audit objective. The project was completed within the timeframe established in the initial version of the plan and all the milestones established throughout the project were achieved.
In relation to the technical part, it was the first time that we worked with a simple form to make the provisioning process more flexible, which has been used in subsequent implementations. We have worked with the User Access Review module and it has been proven that it is a tool that can fulfill the objective of access recertification as long as a correct selection of the roles to be reviewed is made (it is necessary to have a role model with approved positions).